“Cam-out”? “Prevailing torque”? We will explain the terminology related to screws
|
thread forming screw |
Screws that can be screwed into unthreaded holes (pre-drilled holes) while allowing the screw itself to plastically form the female thread. |
|
self-tapping |
Threading a female thread into a mating material while allowing it to be plastically formed. |
|
mating material |
A member with a female screw or pre-drilled hole that is tightened with a screw to fasten the member. |
|
fastening component (clamped part) |
A component or part that is inserted between the head of a tapping screw and the mating material. |
|
pilot hole diameter |
Diameter of mating material preparation hole required for self-tapping |
|
thrust loading |
Thrusting force in the axial direction of a screw when fastening a screw |
|
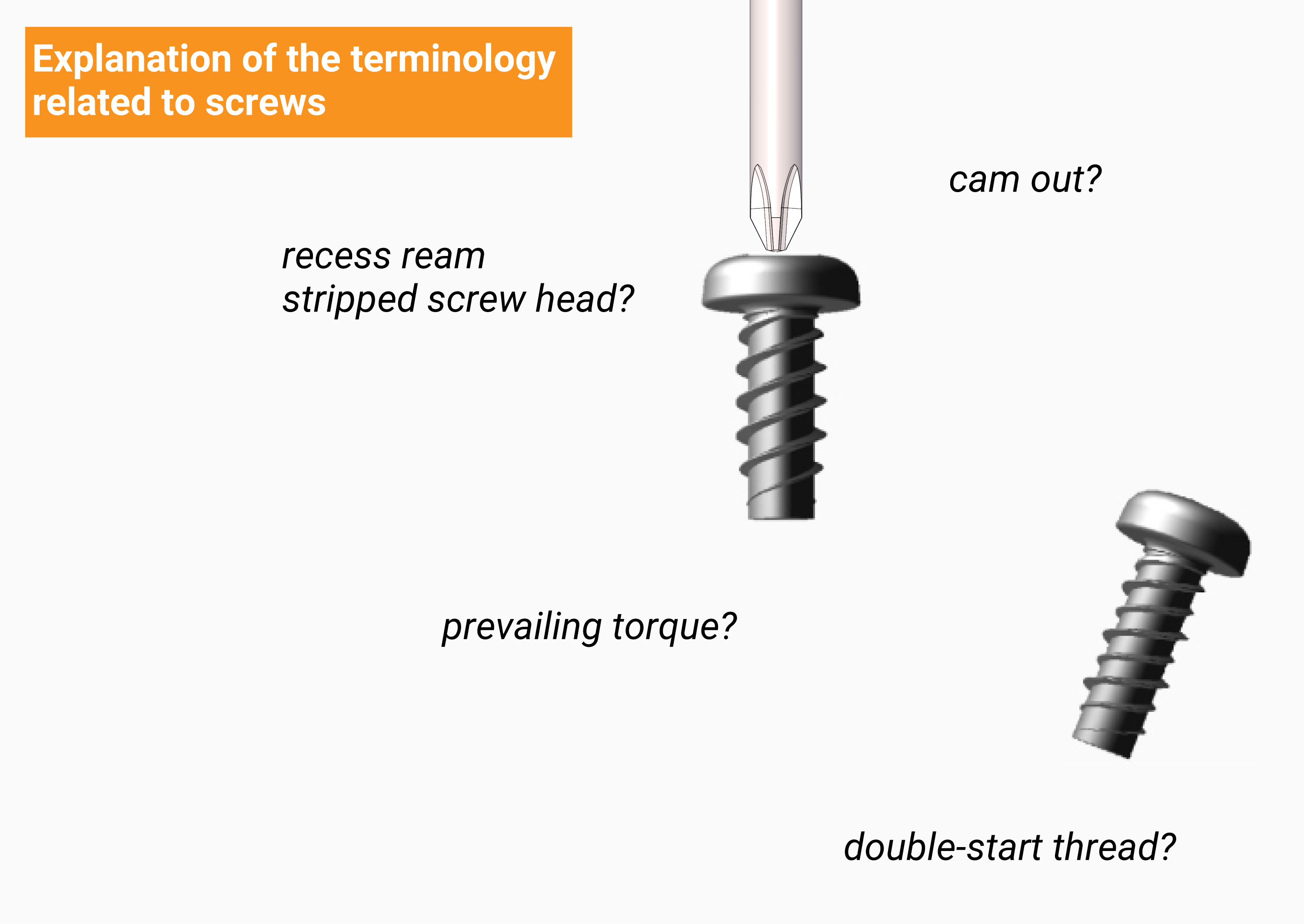
cam out |
Insufficient force (thrust) to push the screw forward, causing the bit to lift off the crosspiece |
|
recess ream stripped screw head |
Cross-holes are crushed when tightening the cross-holes with a bit |
|
torsional strength |
Torque when twisting and breaking the screw itself |
|
tightening torque |
The torque required to screw a screw to obtain a given tightening force. |
|
driving torque |
The maximum value of torque required for a tapping screw to form a female thread in a mating material's downhole. |
|
(thread) stripping torque |
The maximum torque that can be applied to a thread or male screw molded into a mating material before it is broken. |
|
drive-to-strip torque ratio |
Ratio of starting torque to tightening breaking torque |
|
loosening torque |
Maximum torque required to loosen a screw after tightening to a specified tightening torque |
|
torque ratio of tightening loosening |
Ratio of Tightening Torque to loosening Torque |
|
axial tension |
The force applied in the axial direction of the screw, the strength of the fastening that compresses the fastening component. |
|
withstanding axial external force |
The maximum external force that a molded thread or male thread can withstand without breaking when an external force is applied in the axial direction from the opposite direction of the screwing in of a fastener fastened with a tapping screw. |
|
prevailing torque |
Frictional torque generated by interference between the threaded part of a male screw and female screw. |
|
taper |
An imperfectly threaded part where the threads are gradually reduced to improve screw threading performance at the tip of the screw. |
|
plain sheared end |
The tip of the male screw, without the tapered section, as it is after thread rolling |
|
lead angle |
The angle formed by the screw axis and the helix (screw thread line). |
|
pitch |
The distance between adjacent screw threads |
|
double-start thread |
A screw with two helix (screw threaded line) that advances two pitches per rotation. |
|
percentage of thread engagement |
The ratio of the height of the female screw thread (female screw thread height) to the height of the male screw thread (male screw thread height) |
